During the Cretaceous Period, Pangea continued to split, resembling the continents we know today. North America, South America, Africa, Asia, and Europe began to take shape.
Climate
The climate continued to stay hot and muggy; however, the water level began to rise. This added water helped form more swamps, another ecological boost in which dinosaurs could prosper.
Plants
The Cretaceous Period saw the evolution of flowering plants, which spread across the separating continents. Forests became thicker and other kinds of dense, matted vegetation spurted as well. Unfortunately at the end of the Cretaceous Period, a meteor hit the earth which raised huge clouds of dust. These clouds blot out the sun and caused most of this vegetation to die out. The herbivorous dinosaurs that fed on the plants died, as did the carnivorous dinosaurs that fed on the herbivorous dinosaurs. The way was now clear for the evolution of mammals.
Avian (Flying)

Life
By the end of the Cretaceous Period, Pterosaurs had grown to enormous sizes, rivaling land and water dinosaurs. Quetzalcoatlus, being the most spectacular example, is pictured below. This was the end of the breed, though, as they were gradually crowded out of the sky by the first true birds. 
Aquatic (Living in water)
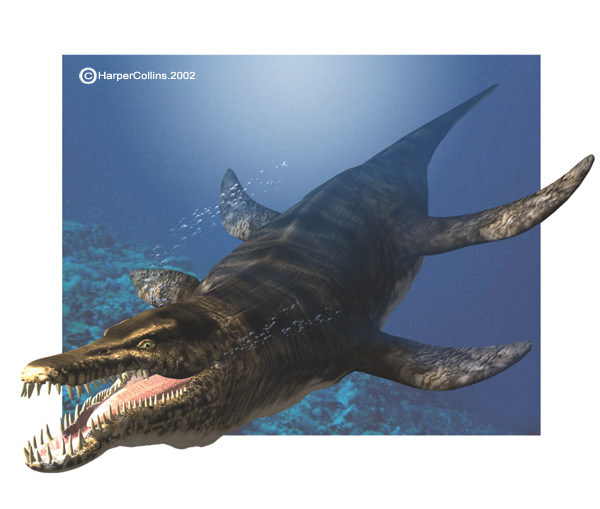
At the beginning of the Cretaceous, many species of the Jurassic Period were no longer around. Instead, giant Pliosaurs, like Kronosaurs (pictured below), came into sight. Kronosaurus preyed on fish, squids and mollusks. A new breed of bony fish, known as teleosts, roamed the seas in enormous schools.


Terrestrial (Living on land)
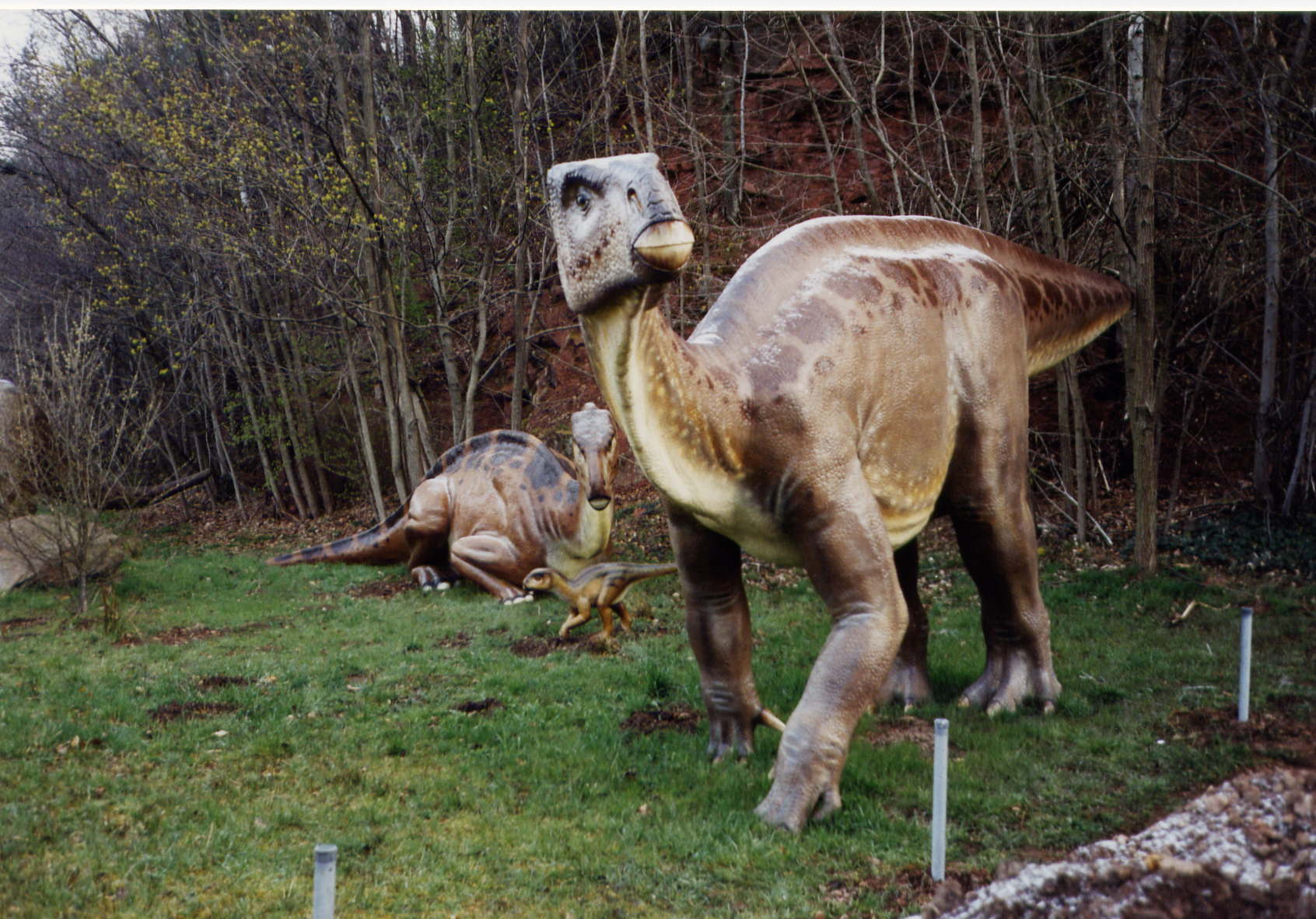
The spread of diverse dinosaurs expanded during the Cretaceous Period. Thousands of creatures roamed the slowly separating continents, including T. Rex, Iguanodon, and Triceratops. 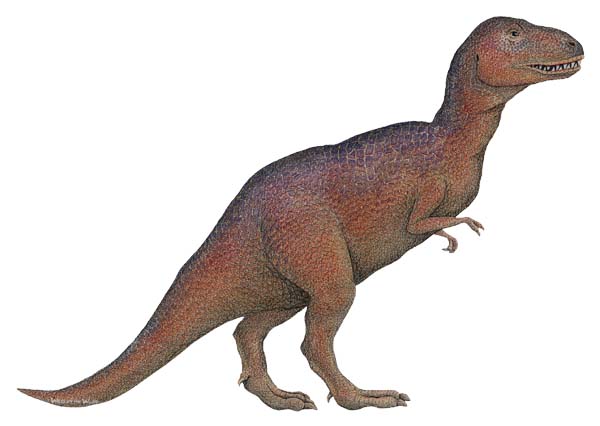

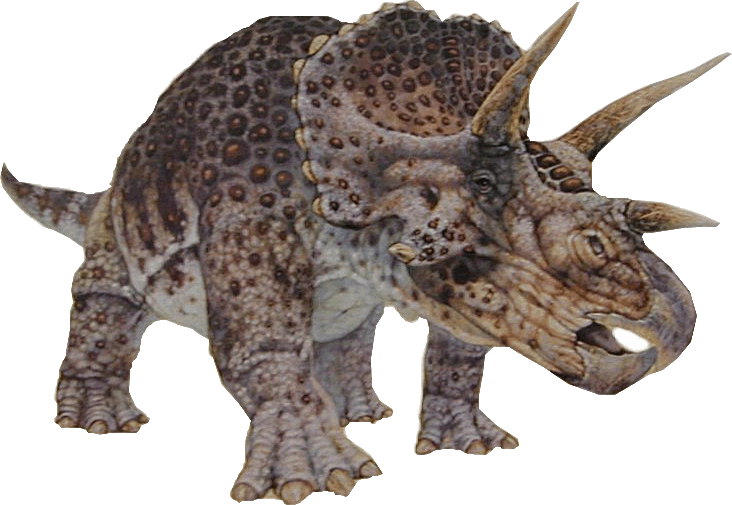
Mammals still kept to themselves; they would only emerge from the shadows after the dinosaurs were wiped out in the K/T Extinction.
Step 1: Home
Return to Step 3: Process